Problem: We are given a rod of length l and an array that contains the prices of different sizes less than l. Our task is to piece the rod in such a way that the revenue generated by selling them is maximum.
For example, consider following given problem:
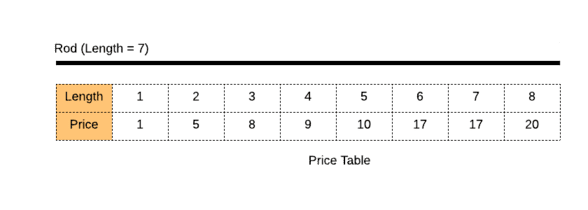
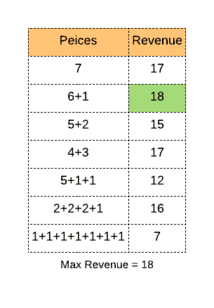
We could get a maximum revenue of 18 if we cut the rod into two pieces of length 6 and 1.
We can solve this problem using recursion and further optimize it using dynamic programming.
Solution using Recursion (Naive Approach)
We can cut a rod of length l at position 1, 2, 3, …, l-1 (or no cut at all).
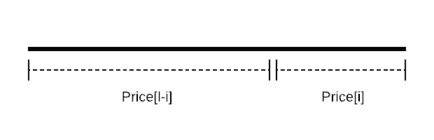
In each case, we cut the rod and sum the prices of the pieces. We compare the total revenue of each case and get the one which gives the maximum profit.
i.e., max(price[l-i] +price[i]) for all i in {0, 1 … l-1}
Because every piece after the cut is a rod itself, we recursively repeat the same process to get the max possible revenue for each piece.
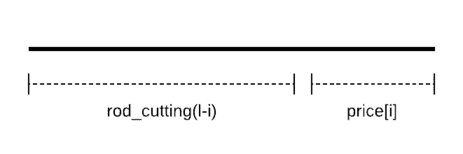
i.e., max(rod_cutting(l-i]) +price[i]) for all i in {0, 1 … l-1}
Here is the implementation of the recursive solution in Python, C++ and Java:
Python
import sys
#list of prices corresponding to the peices of index length
price = [0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20];
#recursive Solution
def rod_cutting(l):
#base condition
if(l==0):
return 0
#variable to store the maximum revenue
max_value = -sys.maxsize
#loop for all possible cut cases
for i in range(1, l+1):
#store the max revenue of all cut cases
max_value = max(max_value, rod_cutting(l-i)+ price[i])
return max_value
#Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("Max Revenue: ",rod_cutting(7))C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//array of prices corresponding to the pieces of index length
int price[]= {0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20};
//recursive function
int rod_cutting(int l){
//base condition
if(l==0)
return 0;
//variable to store max revenue,
//initially have minimum possible integer value
int max_value = INT32_MIN;
//loop for all possible cut cases
for(int i=1; i<=l; i++){
//store the max revenue of all cut cases
max_value = max(max_value, rod_cutting(l-i)+ price[i]);
}
return max_value;
}
//Driver code
int main() {
cout << "Max Revenue: " << rod_cutting(7);
return 0;
}
Java
class Main {
//array of prices corresponding to the pieces of index length i.e, price table
static int price[]= {0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20};
//Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Max Revenue: "+rod_cutting(4));
}
//Recursive function
public static int rod_cutting(int l){
//Base condition
if(l==0)
return 0;
//variable to store max revenue,
//initially have minimum possible integer value
int max_value = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//loop for all possible cut cases
for(int i=1; i<=l; i++){
//store the max revenue of all cut cases
max_value = Math.max(max_value, rod_cutting(l-i)+ price[i]);
}
//return the max value
return max_value;
}
}The time complexity of the above solution is O(nn).
The reason for such high time complexity is that the recursive solution computes overlapping subproblems multiple times.
For instance, when computing the max price of length=7, the price of some of the preceding lengths is calculated multiple times.
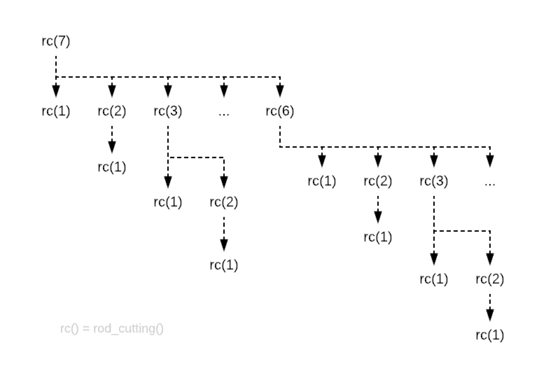
We can leverage dynamic programming to significantly reduce the computational task of the recursive solution.
Solution using Dynamic Programming (Efficient Approach)
The idea is to store the solution of subproblems into a memo table (array) so that we can reuse them without computing it again i.e., store the max price of each length into an array when they are calculated for the first time.
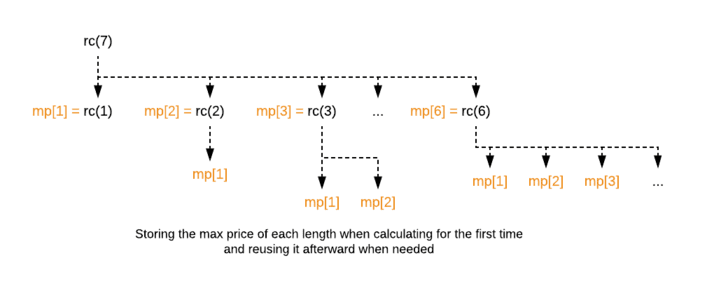
Here is the implementation of the solution of the rod cutting problem using Dynamic Programming:
Python
import sys
#list of prices corresponding to the peices of index length
price = [0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20]
#memo table
max_price = [-1 for x in range(len(price))]
#recursive funtion
def rod_cutting(l):
#base condition
if(l==0):
return 0
#check memo table if it already has the max price for length 'l'
#if yes then return the value otherwise continue computing the max price for 'l'
if max_price[l] != -1:
return max_price[l]
#variable to store the maximum revenue
max_value = -sys.maxsize
#loop for all possible cut cases
for i in range(1, l+1):
#store the max revenue of all cut cases
max_value = max(max_value, rod_cutting(l-i)+ price[i])
#update the max price for 'l' in the memo table
max_price[l] = max_value
return max_price[l]
#Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
length = 7
print("Max Revenue: ",rod_cutting(length))
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//array of prices corresponding to the peices of index length
int price[]= {0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20};
//memo table to store max price each lengths
int max_price[sizeof(price)/sizeof(price[0])];
//recursive function
int rod_cutting(int l){
//base condition
if(l==0)
return 0;
//check memo table if it already has the max price for length 'l'
//if yes then return the value otherwise continue computing the max price for 'l'
if(max_price[l] != 0)
return max_price[l];
//variable to store max revenue,
//initially have minimum possible integer value
int max_value = INT32_MIN;
//loop for all possible cut cases
for(int i=1; i<=l; i++){
//store the max revenue of all cut cases
max_value = max(max_value, rod_cutting(l-i)+ price[i]);
}
//store the max price for 'l' in the memo table
max_price[l] = max_value;
//return the max price
return max_price[l];
}
//Driver code
int main() {
int length = 7;
cout << "Max Revenue: " << rod_cutting(length);
return 0;
}
Java
class Main {
//array of prices corresponding to the peices of index length i.e, price table
static int price[]= {0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20};
//memo table to store max price each lengths
static int max_price[] = new int[price.length];
//Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int length = 7;
System.out.println("Max Revenue: "+rod_cutting(length));
}
//Recursive function
public static int rod_cutting(int l){
//Base condition
if(l==0)
return 0;
//check memo table if it already has the max price for length 'l'
//if yes then return the value otherwise continue computing the max price for 'l'
if(max_price[l] != 0)
return max_price[l];
//variable to store max revenue,
//initially have minimum possible integer value
int max_value = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//loop for all possible cut cases
for(int i=1; i<=l; i++){
//store the max revenue of all cut cases
max_value = Math.max(max_value, rod_cutting(l-i)+ price[i]);
}
//store the max price for 'l' in the memo table
max_price[l] = max_value;
//return the max price
return max_price[l];
}
}Output:
Max Revenue: 18The time complexity of this solution is O(n2). Since we are using an extra array for memorization, the space complexity for the program is O(n).
In this tutorial, we learned to solve the rod cutting problem using the concept of dynamic programming in C++, Java, and Python.