Problem: Given an unweighted undirected graph, find the shortest path from the given source to the given destination using the depth-first search algorithm.
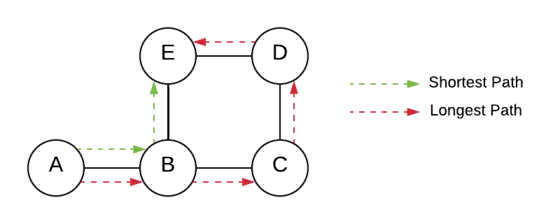
Since the graph is undirected and connected, there is at least one path between any two vertices of the graph. Therefore it is possible to find the shortest path between any two vertices using the DFS traversal algorithm.
The idea is to successively seek for a smaller path from source to destination vertex using the DFS algorithm.
We explore all possible paths and compare them based on their length. The one with the shortest length is the shortest path between the given vertices.
How to compare length of the possible paths?
We use an integrer length variable to keep count of the number of vertices in the active route (depth) of DFS.
Every time we visit a vertex we increment it by 1.
If the vertex that is being visited is the destination vertex, we compare it with the shortest length of all the discovered paths by then.
How to get route of the shortest path?
we use an extra node property called prev that stores the reference of the preceding vertex for each vertex.
Every time we visit a vertex, we also update its prev value with the last visited vertex.
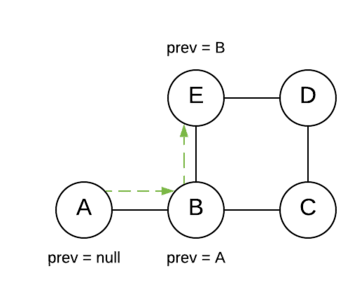
Using the prev value, we trace the route back from the end vertex to the starting vertex. Example for the given graph, route = E <- B <- A.
Let’s see the implementations of this approach in Python, C++ and Java.
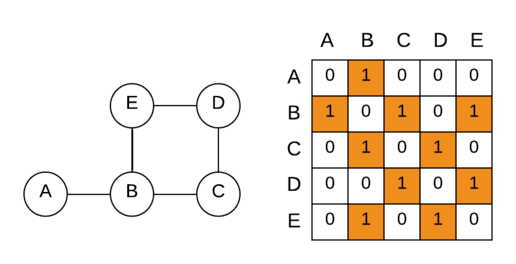
Shortest Path in Graph represented using Adjacency Matrix
Adjacency Matrix is an 2D array that indicates whether the pair of nodes are adjacent or not in the graph.
Python
import sys
class ShortestPath:
def __init__(self, start, end):
self.start = start
self.end = end
self.shortLength = sys.maxsize
def findPath(self):
#start DFS from the start vertex
self.dfs(self.start)
#trace the route to output the path
self.trace_route()
def dfs(self, vertex):
global length
#Increment the current path length by 1
length +=1
#1st base condition
#return if current route is longer
#than the already discovered route
if length > self.shortLength:
return
#2nd base condition
#if reach the destination vertex
#update the shortLength and
#return to explore shorter routes
if vertex == self.end:
self.shortLength = length
return
#mark vertex as visited to prevent overvisit
visited[vertex] = 1
#iterate through all unvisited neighbors vertices
for i in range(N):
if adjacencyM[vertex][i] == 1 and visited[i] == 0:
nbr = i
#update the preceding vertex of the neighbors
prev[nbr] = vertex
#recursively visit the neighbors
#to continue search for the destination vertex
self.dfs(nbr)
#backtrack
#visited[vertex] = 0
length -=1
#Function to trace the route using preceding nodes
def trace_route(self):
vertex = self.end
route = []
#start node has no preceding node
#so loop until node->prev is null
while vertex != -1:
route.append(vertices_names[vertex])
vertex = prev[vertex]
#reverse the route bring start to the front
route.reverse()
#output route
print(route)
if __name__ == '__main__':
#vertices or nodes
vertices_names = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'];
#number of vertices
N = len(vertices_names)
#Adjacency Matrix
adjacencyM = [[0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1 ,0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0]];
#List mapping of vertices to mark them visited
visited = [0 for x in range(N)]
#List to stores preceding vertices
prev = [-1 for x in range(N)]
#Driver code
sp = ShortestPath(0, 4)
length = 0
sp.findPath()C++
#include <iostream>
#include<list>
#define N 5
using namespace std;
//vertices or nodes
char vertices_names[] = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'};
//Adjacency Matrix
int adjacencyM[N][N] = {{0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 1 ,0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}};
class ShortestPath{
//array to store preceding nodes
int prev[N] = {-1};
//array mapping to make visited vertices
int visited[N] = {0};
//start and end nodes index
int start, end;
//variable to store length of the current route
int length = 0;
//variable to store length of the shortest route
int shortLength = INT32_MAX;
public:
ShortestPath(int start, int end){
this->start = start;
this->end = end;
}
void findPath(){
//start DFS from the start vertex
dfs(start);
//trace the route to output the path
trace_route();
}
private:
void dfs(int vertex){
//Increment the current path length by 1
length +=1;
//1st base condition
//return if current route is longer
//than the already discovered route
if(length > shortLength)
return;
//2nd base condition
//if reach the destination vertex
//update the shortLength and
//return to explore shorter routes
if(vertex == end){
shortLength = length;
return;
}
//mark vertex as visited to prevent overvisit
visited[vertex] = 1;
//iterate through all unvisited neighbors vertices
for(int i=0; i<N; i++){
if(adjacencyM[vertex][i] == 1 and visited[i] == 0){
int nbr = i;
//update the preceding vertex of the neighbors
prev[nbr] = vertex;
//recursively visit the neighbors
//to continue search for the destination vertex
dfs(nbr);
}
}
//decrement length when tracing back
length -=1;
}
//Function to trace back route
void trace_route(){
list<char> route;
int vertex = end;
//start node has no preceding vertex
//so loop until prev[vertex] is -1
while(vertex != -1){
route.push_front(vertices_names[vertex]);
vertex = prev[vertex];
}
//Display the route
for(char n: route){
cout << n <<" ";
}
}
};
int main()
{
//Driver Code
ShortestPath shortestPath(0, 4);
shortestPath.findPath();
}Java
import java.util.*;
class ShortestPath{
//Adjacency matrix
int adjacencyM[][];
//vertices labels
char vertices_names[];
//array to store preceding nodes of the traversed vertices
int prev[];
//array mapping to make visited vertices
int visited[];
//start and end vertices index
int start, end;
//variable to store length of the current route
int length = 0;
//variable to store length of the shortest route
int shortLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
ShortestPath(int adjacencyM[][], char[] vertices, int start, int end){
this.adjacencyM = adjacencyM;
this.vertices_names = vertices;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
this.visited = new int[vertices.length];
this.prev = new int[vertices.length];
Arrays.fill(this.prev, -1);
}
public void findPath(){
//start DFS from the start vertex
dfs(start);
//trace the route to output the path
trace_route();
}
private void dfs(int vertex){
//Increment the current path length by 1
length +=1;
//1st base condition
//return if current route is longer
//than the already discovered route
if(length > shortLength)
return;
//2nd base condition
//if reach the destination vertex
//update the shortLength and
//return to explore shorter routes
if(vertex == end){
shortLength = length;
return;
}
//mark vertex as visited to prevent overvisit
visited[vertex] = 1;
//iterate through all unvisited neighbors vertices
for(int i=0; i<adjacencyM.length; i++){
if(adjacencyM[vertex][i] == 1 && visited[i] == 0){
int nbr = i;
//update the preceding vertex of the neighbors
prev[nbr] = vertex;
//recursively visit the neighbors
//to continue search for the destination vertex
dfs(nbr);
}
}
//decrement length when tracing back
length -=1;
}
//Function to trace route using preceding nodes
private void trace_route(){
int vertex = end;
List<Character> route = new ArrayList<>();
//start vertex has no preceding vertex
//so loop until prev[vertex] is -1
while(vertex!=-1){
route.add(vertices_names[vertex]);
vertex = prev[vertex];
}
//Reverse route to bring start vertex at front
Collections.reverse(route);
//Output the route
System.out.println(route);
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//vertices or nodes array
char vertices[] = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'};
//Adjacency Matrix
int adjacencyM[][] = {{0, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 1},
{0, 0, 1 ,0, 1},
{0, 1, 0, 1, 0}};
//Driver Code
ShortestPath shortestPath = new ShortestPath(adjacencyM, vertices, 0, 4);
shortestPath.findPath();
}
}Output:
[A, B, E]In the above program, the visited array keeps records of the visited vertices and the prev array holds the preceding vertex of each vertex on the corresponding index.
In one of the base conditions, when the length of the active DFS route exceeds the length of the smallest path ever discovered, we deliberately return to look for another way.
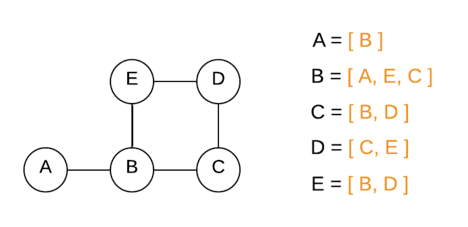
Shortest Path in Graph represented using Adjacency List
Every vertex of the graph holds a list of its neighbor (connected) vertices.
Python
import sys
#class representing vertex of a graph
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, name):
#vertex label
self.name = name
#variable to hold preceding vertex reference
self.prev = None
#variable to mark vertex as visited
self.visited = False
#adjacency list
self.neighbors = []
#Method to connect nodes (undirected)
def add_neighbor(self, node):
self.neighbors.append(node)
node.neighbors.append(self)
#String representaion of vertex class
def __repr__(self):
return self.name
class ShortestPath:
def __init__(self, start, end):
#start vertex
self.start = start
#end vertex
self.end = end
#hold the length of the active route in DFS
self.length =0
#variable to store length of the shortest route
self.shortLength = sys.maxsize
def findPath(self):
#start DFS from the start vertex
self.dfs(self.start)
#trace the route to output the path
self.trace_route()
def dfs(self, vertex):
#Increment the current path length by 1
self.length +=1
#1st base condition
#return if current route is longer
#than the already discovered route
if self.length > self.shortLength:
return
#2nd base condition
#if reach the destination vertex
#update the shortLength and
#return to explore shorter routes
if vertex == self.end:
self.shortLength = self.length
return
#mark vertex as visited to prevent overvisit
vertex.visited = True
#iterate through all unvisited neighbors vertices
for nbr in vertex.neighbors:
if not nbr.visited:
#update the preceding vertex of the neighbors
nbr.prev = vertex
#recursively visit the neighbors
#to continue search for the destination vertex
self.dfs(nbr)
#decrement length when tracing back
self.length -=1
#Function to trace the route using preceding nodes
def trace_route(self):
node = self.end
route = []
#start node has no preceding node
#so loop until node->prev is null
while node:
route.append(node)
node = node.prev
#reverse the route bring start to the front
route.reverse()
#output route
print(route)
if __name__ == '__main__':
#vertices
vertices = [Vertex('A'), Vertex('B'), Vertex('C'), Vertex('D'), Vertex('E')]
#connect nodes (i.e. create graph)
vertices[0].add_neighbor(vertices[1])
vertices[1].add_neighbor(vertices[2])
vertices[2].add_neighbor(vertices[3])
vertices[3].add_neighbor(vertices[4])
vertices[1].add_neighbor(vertices[4])
#driver code
shortestPath = ShortestPath(vertices[0], vertices[4])
shortestPath.findPath()C++
#include <iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
//class representing vertex of a graph
class Vertex{
public:
//vertex label
char name;
//variable to mark vertex as visited
bool visited = false;
//variable to hold preceding vertex reference
Vertex* prev = nullptr;
//Adjacency List of the vertex
list<Vertex*> neighbors;
Vertex(char name){
this->name = name;
}
//Method to connect vertices (undirected)
void add_neighbor(Vertex* v){
this->neighbors.push_back(v);
v->neighbors.push_back(this);
}
};
class ShortestPath{
//start vertex
Vertex* start;
//end vertex
Vertex* end;
//variable to store length of the current route
int length = 0;
//variable to store length of the shortest route
int shortLength = INT32_MAX;
public:
ShortestPath(Vertex* start, Vertex* end){
this->start = start;
this->end = end;
}
void findPath(){
//start DFS from the start vertex
dfs(start);
//trace the route to output the path
trace_route();
}
private:
void dfs(Vertex* vertex){
//Increment the current path length by 1
length +=1;
//1st base condition
//return if current route is longer
//than the already discovered route
if(length > shortLength)
return;
//2nd base condition
//if reach the destination vertex
//update the shortLength and
//return to explore shorter routes
if(vertex == end){
shortLength = length;
return;
}
//mark vertex as visited to prevent overvisit
vertex->visited = true;
//iterate through all unvisited neighbors vertices
for(Vertex* nbr: vertex->neighbors){
if(!nbr->visited){
//update the preceding vertex of the neighbors
nbr->prev = vertex;
//recursively visit the neighbors
//to continue search for the destination vertex
dfs(nbr);
}
}
//decrement length when tracing back
length -=1;
}
//Function to trace back route
void trace_route(){
list<char> route;
Vertex* vertex = end;
//start vertex has no preceding vertex
//so loop until vertex-> is null
while(vertex != nullptr){
route.push_front(vertex->name);
vertex = vertex->prev;
}
//Display the route
for(char n: route){
cout << n <<" ";
}
}
};
int main()
{
//vertices
Vertex* vertices[] = {new Vertex('A'), new Vertex('B'),new Vertex('C'),new Vertex('D'),new Vertex('E')};
//connect vertices (i.e. create graph)
vertices[0]->add_neighbor(vertices[1]);
vertices[1]->add_neighbor(vertices[2]);
vertices[2]->add_neighbor(vertices[3]);
vertices[3]->add_neighbor(vertices[4]);
vertices[1]->add_neighbor(vertices[4]);
//Driver Code
ShortestPath shortestPath(vertices[0], vertices[4]);
shortestPath.findPath();
}Java
import java.util.*;
//Class representing a vertex of a graph
class Vertex{
//vertex label
String name;
//Adjacency List
List<Vertex> neighbors;
//variable to mark vertex as visited
boolean visited = false;
//variable to hold preceding vertex reference
Vertex prev = null;
Vertex(String name){
this.name = name;
this.neighbors = new ArrayList<>();
}
//Method to connect vertices
void add_neighbor(Vertex vertex){
this.neighbors.add(vertex);
vertex.neighbors.add(this);
}
//String representation of the class
public String toString(){
return this.name;
}
}
class ShortestPath{
//start and end vertex
Vertex start, end;
//variable to store length of the current route
int length = 0;
//variable to store length of the shortest route
int shortLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
ShortestPath(Vertex start, Vertex end){
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
void findPath(){
//start DFS from the start vertex
dfs(start);
//trace the route to output the path
trace_route();
}
private void dfs(Vertex vertex){
//Increment the current path length by 1
length +=1;
//1st base condition
//return if current route is longer
//than the already discovered route
if(length > shortLength)
return;
//2nd base condition
//if reach the destination vertex
//update the shortLength and
//return to explore shorter routes
if(vertex == end){
shortLength = length;
return;
}
//mark vertex as visited to prevent overvisit
vertex.visited = true;
//iterate through all unvisited neighbors vertices
for(Vertex nbr: vertex.neighbors){
if(!nbr.visited){
//update the preceding vertex of the neighbors
nbr.prev = vertex;
//recursively visit the neighbors
//to continue search for the destination vertex
dfs(nbr);
}
}
//decrement length when tracing back
length -=1;
}
//Function to trace the route
private void trace_route(){
Vertex vertex = end;
List<Vertex> route = new ArrayList<>();
//preceding vertex of start vertex is null
//becasue start.prev == null
while(vertex != null){
route.add(vertex);
vertex = vertex.prev;
}
//Reverse the route bring start to the front
Collections.reverse(route);
//Output the route
System.out.println(route);
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//vertices
Vertex vertices[] = {new Vertex("A"), new Vertex("B"),new Vertex("C"),new Vertex("D"),new Vertex("E")};
//connect vertices (i.e. create graph)
vertices[0].add_neighbor(vertices[1]);
vertices[1].add_neighbor(vertices[2]);
vertices[2].add_neighbor(vertices[3]);
vertices[3].add_neighbor(vertices[4]);
vertices[1].add_neighbor(vertices[4]);
//Driver Code
ShortestPath sp = new ShortestPath(vertices[0], vertices[4]);
sp.findPath();
}
}Output:
[A, B, E]In this method, we represented the vertex of the graph as a class that contains the preceding vertex prev and the visited flag as a member variable.
The time complexity of finding the shortest path using DFS is equal to the complexity of the depth-first search i.e. O(V+E) because in the worst case the algorithm has to cross every vertices and edges of the graph.
you spelled integer as integrer