Problem: Write a c program to add two matrices using linked list.
Each node of the linked list represent a matrix element, where:
- row – Stores the row value of the element.
- col – Stores the column value of the element.
- data – Store the value of the element.
- *next -Store the address of next element (node).
The following code add two matrices in C using the concept of linked list..
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct element
{
int row;
int col;
int data;
struct element *next;
}element;
typedef struct matrix
{
element *head;
int rows;
int columns;
element *tail;
int nodecount;
}matrix;
// prototype definition
void init(matrix *,int,int);
void creatematrice(matrix *,int,int,int);
int searchdata(matrix *,int,int);
matrix* addmatrix(matrix *, matrix *);
void display(matrix *);
matrix finalmatrix;
void init(matrix *m,int r,int c)
{
m->head=NULL;
m->tail=NULL;
m->columns=c;
m->rows=r;
m->nodecount=r*c;
}
void creatematrice(matrix *m,int d,int r,int c)
{
element *current=(element *)malloc(sizeof(element));
current->row=r;
current->col=c;
current->data=d;
current->next=m->head;
m->head=current;
}
matrix* addmatrix(matrix *m1,matrix *m2)
{
if(m1->head == NULL || m2->head == NULL)
{
printf("addition not possible as matrix is empty");
return NULL;
}
init(&finalmatrix,m1->rows,m1->columns);
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=m1->rows;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=m2->columns;j++)
{
creatematrice(&finalmatrix,(searchdata(m1,i,j)+searchdata(m2,i,j)),i,j);
}
}
return (&finalmatrix);
}
int searchdata(matrix *m,int r,int c)
{
element *current=m->head;
while(current!=NULL)
{
if(current->col==c && current->row==r)
return current->data;
current=current->next;
}
}
void display(matrix *m)
{
if(m->head == NULL){
printf("Matrix is empty \n");
return;
}
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=m->rows;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=m->columns;j++)
{
printf("%d ",searchdata(m,i,j));
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int ch,r1,r2,c1,c2,ch2,p,s,data,i,j;
matrix m1,m2;
while(1)
{
outer:
printf("1.To enter values in first matrix \n");
printf("2.To enter values in second matrix\n");
printf("3.To add two matrix\n");
printf("4.To display a matrix\n");
printf("5.To exit \n");
printf("Enter choice\n");
scanf("%d",&ch);
switch(ch)
{
case 1:
printf("Enter number of rows\n");
scanf("%d",&r1);
printf("Enter number of columns\n");
scanf("%d",&c1);
init(&m1,r1,c1);
p=r1;
s=c1;
for(i=1;i<=p;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=s;j++)
{
printf("Enter data in %d row %d column ",i,j);
scanf("%d",&data);
creatematrice(&m1,data,i,j);
}
}
printf("First matrix is full\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("Enter number of rows\n");
scanf("%d",&r2);
printf("Enter number of columns\n");
scanf("%d",&c2);
init(&m2,r2,c2);
p=r2;
s=c2;
for(i=1;i<=p;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=s;j++)
{
printf("Enter data in %d row %d column ",i,j);
scanf("%d",&data);
creatematrice(&m2,data,i,j);
}
}
printf("Second matrix is full\n");
break;
case 3:
if(r1!=0 && r2!=0 && c1!=0 && c2!=0 && r1==r2 && c1==c2)
{
matrix *resultmatrix=addmatrix(&m1,&m2);
display(resultmatrix);
}
else
printf("Operation could not be implemented now, may be because of unmatching order\n");
break;
case 4:
while(1)
{
printf("1. To display first matrix\n");
printf("2. To display second matrix\n");
printf("3. To main menu\n");
printf("Enter choice\n");
scanf("%d",&ch2);
switch(ch2)
{
case 1:
display(&m1);
break;
case 2:
display(&m2);
break;
case 3:
goto outer;
default:
printf("Wrong choice\n");
}
}
break;
case 5:
exit(0);
break;
default:
printf("Wrong choice\n");
}
}
}Output
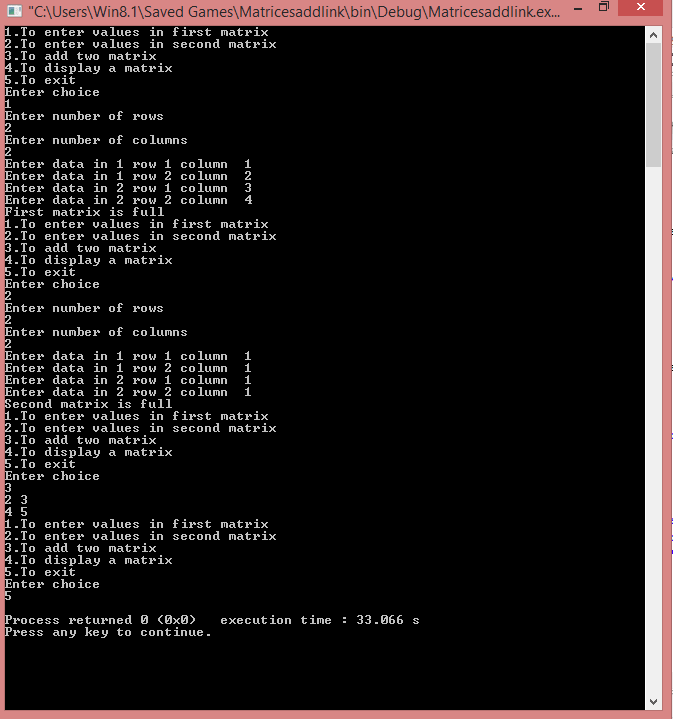
Case 1: When the order of the two matrix are the same.
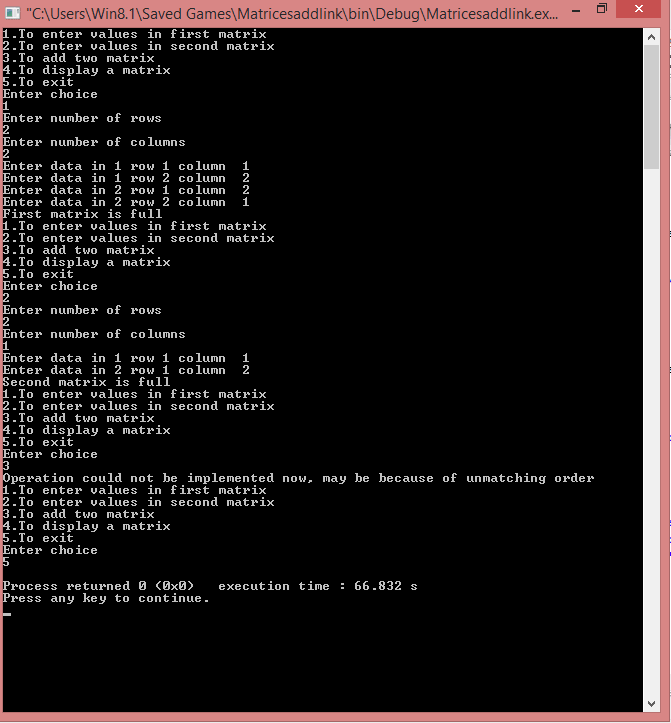
Case 2: When the order of the two matrices is not the same.
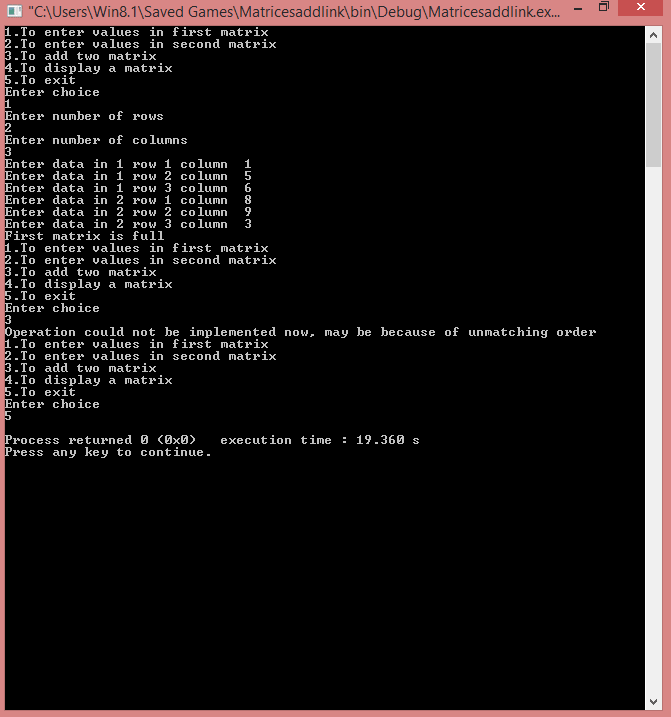
Case 3: When one of the matrices is empty.
In this program, we are using two matrices. Each matrix has:
- rows – Stores the count of the total number of rows in the matrix.
- columns – Stores the count of the total number of columns in the matrix.
- *head – Sores the head element.
- *tail – Stores the tail element.
The program displays the menu in the loop which can handle multiple operations like
- Displaying matrix.
- Inputting elements into the matrix.
- Adding two matrix.
- Exit & more.
I recommend you to run the code with different inputs to understand the code at best.