Summary: In this post, we will learn what inheritance is and how can we inherit a class to another in C++.
Introduction to Inheritance
Inheritance is one of the important features of any object-oriented programming language.
It promotes code reusability by allowing one class to reuse the properties and functions of another class.
Instead of rewriting, we can use reuse the code of another class.
For example, if there is a method in class A that we want to reuse in class B, we can inherit Class A in Class B to gain access to that method.
Let’s see this in action in C++:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Account{
public:
double balance = 157832;
};
class SavingsAccount: public Account{
public:
void displayBalance(){
//reusing balance of the Account class
cout << "Balance: " << balance;
}
};
int main(){
SavingsAccount sa;
sa.displayBalance(); //outputs Balance: 157832
return 0;
}Notice, we didn’t define the balance variable in the SavingAccount class, but were still able to output it from the displayBalance method.
It is because we have inherited the Account class in the SavingAccount class.
How to Inherit a class in C++?
To inherit a class in C++, in the class declaration we write the mode of inheritance after a colon (:) followed by the name of the class which we are inheriting.
class A{
...
};
class B: <public|protected|private> class B{
...
}; The class that is being derived is known as super, parent, or base class, and the class which is inheriting is called a sub, child, or derived class.
In the above syntax the class
Ais the superclass and classBis the subclass.
Modes of Inheritance
The mode of inheritance in C++ depends on the access specifier used in the declaration of the inheritance statement.
The mode determines the access level of the parent class’s properties in the subclass.
| Public | The access level of the properties in class A remains the same in class B. |
| Protected | The access level of the public properties in class A reduces to protected in class B. |
| Private | The access level of the public and protected properties in class A reduces to private in class B (i.e. all properties of class A become private in class B). |
If any member is public or protected in class A but the mode of inheritance is private, it will become private in class B.
Similarly, if any member is public in class A but the mode of inheritance is protected, its access level will decrease to protected in class B.
Note: Whatever be the mode of inheritance, the private members of the parent class remain inaccessible to the child class.
Consider the following program for example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
char* name = "Pencil Programmer";
protected:
char* dob = "01/30/1996";
private:
char* password = "******";
};
class B: private A {
public:
void displayDetails(){
//name and dob is now private in this class
cout << "Name: " << name << "\n";
cout << "DOB: " << dob << "\n";
//Error: we cannot access the private members of the base class
//cout << "Password: " << password;
}
};
int main(){
B().displayDetails();
return 0;
}Here, we cannot access the password (private) property of class A in class B. If we try to do so, the compiler will throw an error.
We were able to use the name and dob properties of class A (because they were not private) in class B, but since the mode of inheritance is private here, their access level also becomes private in class B.
Types of Inheritance in C++
The types of inheritance in C++ depend on what classes we are inheriting.
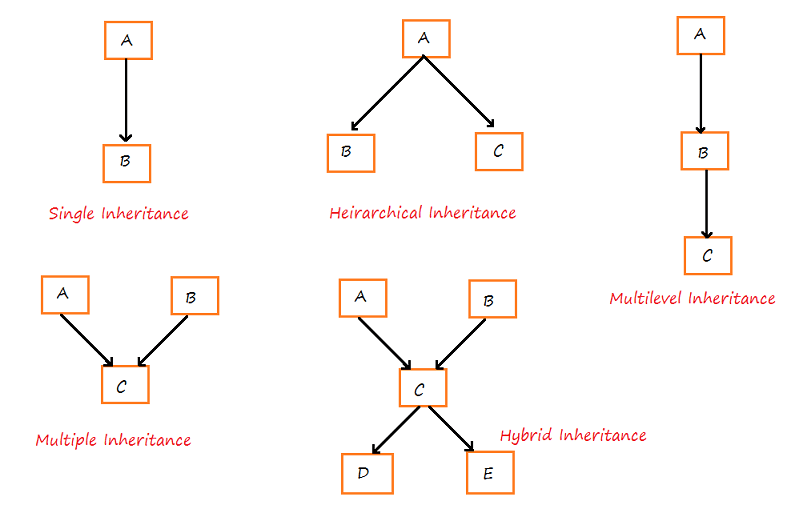
Since C++ allows inheriting multiple classes, we can classify inheritance into 5 types:
- Single Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
We should not just inherit classes to implement a type of inheritance but inherit based on the requirements and relationship between the classes.
For example, if there is a possibility of reusing the code of the class in another class that is already a subclass, we can further extend it to multilevel inheritance.
When to use Inheritance?
Inheritance implies IS A relationship between class.
We should check if such a relationship could exist between the classes, if so, then we should inherit accordingly.
For example, the dog is an animal. It would be best to inherit the Animal class in the Dog class.