Summary: In this tutorial, we will learn to create a table in the MySQL database using the command line and phpMyAdmin interface.
According to MySQL documentation, the general syntax to create a table in MySQL is
CREATE TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name( column_1_definition, column_2_definition, ..., table_constraints );
where
IF NOT EXISTSis optional. It ensures that the table will only be created when there is no table of the same name present in the database.column_definitionis the syntax for individual columns.table_constraintsare the optional constraints for the table and columns such as PRIMARY_KEY, UNIQUE_KEY, CHECK, etc.
The general syntax for the column_definition is
column_name data_type(length) [NOT NULL] [DEFAULT value] [AUTO_INCREMENT] [column_constraint];
in which the mandatory part is the name and data type of the column.
So if we want to create a simple table without any constraints then our SQL syntax would be
CREATE TABLE table_name(
column_name data_type(length),
column_name data_type(length),
...,
column_name data_type(length)
);Let’s see some examples for better clarification.
Recommended: How to create a database in MySQL?
Examples
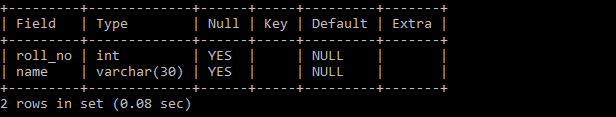
Example 1: Table without any constraints.
create table students (
roll_no int,
name varchar(30)
);
Example 2: Table with a NOT NULL constraint.
create table students (
roll_no int NOT NULL,
name varchar(30)
);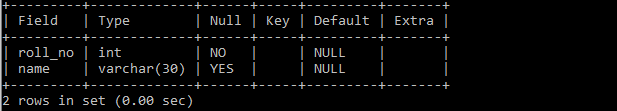
Adding NOT NULL constraint to roll_no column means every record should have a valid roll_no value otherwise the record will not be inserted into the table.
Example 3: Table with a column having a default value.
create table math_marks (
roll_no int NOT NULL,
name varchar(30) NOT NULL,
marks int default 0
);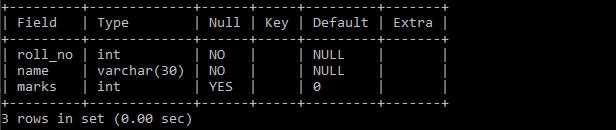
In the above table roll_no and name column is mandatory because of the ‘NOT NULL’ constraint but marks field has a default value of 0, which means if we don’t specify marks of a student at the time of inserting a record then by default 0 will be stored into the respective marks column.
Recommended: Primary Key in MySQL
Example 4: Table with a single column as the primary key.
create table math_marks (
roll_no int PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(30) NOT NULL,
marks int default 0
);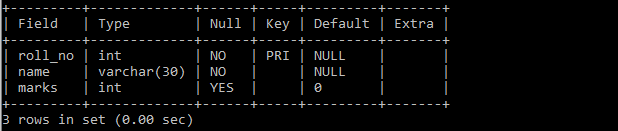
Specifying ‘roll_no’ as a primary key means ‘roll_no’ cannot be null and must be unique i.e each record in the table must have a unique roll_no.
Example 5: Table with multiple columns as the primary key.
create table math_marks (
roll_no int,
name varchar(30),
marks int default 0,
PRIMARY KEY (roll_no, name)
);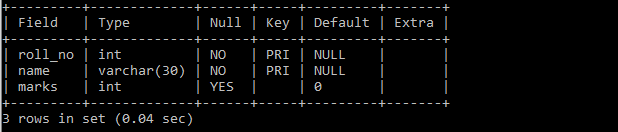
In the above table both roll_no and name together comprise a single primary key for math_marks.
Note: Each table can have a maximum of 1 primary key. The math_marks table has only 1 primary key which is constituted by multiple columns (i.e {roll_no, name}).
Example 6: Table with an AUTO_INCREMENT column.
create table customers (
id int PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name varchar(30) NOT NULL
);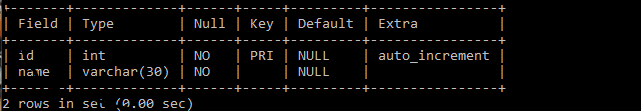
In the above table, the id is an AUTO_INCREMENT column, which means we don’t need to specify the id value while inserting records into the table.
Note: An AUTO_INCREMENT column must be a PRIMARY KEY.
There are various constraints like CHECK, FOREIGN KEY, etc, which need separate discussion and we will discuss that in a separate post. For now, if you have any doubts or suggestions then comment below.