In this post, we will discuss all MySQL Data Types along with their properties, so that at the time of designing a new database, we would be able to use appropriate MySQL data types as per the requirement.
Introduction to MySQL Data Types
The use of proper data type for any column (attribute) plays a crucial role in the performance and scalability of any database.
If you know that a column is not going to have any record with more than 3 characters, then allocating a data type that occupies 10 characters space for each record would be inefficient.
Therefore, the use of appropriate data types for every column in the MySQL table is very important.
So, let us discuss every data type in MySQL in detail.
MySQL support 5 categories of SQL data types which are as follows
- Numeric
- Date and Time
- String (Characters and Bytes)
- Spatial
- JSON.
Now we know what categories of data types are supported in MySQL, so let us discuss each category in detail.
Numeric Data Types in MySQL
MySQL supports all standard SQL numeric data types. These types include the integer data types such as INTEGER, SMALLINT, DECIMAL, and NUMERIC as well as the floating-point numeric data types such as FLOAT, REAL, and DOUBLE.
INTEGER
The following table shows the required storage and range for integer types in MySQL.
| Type | Storage (Bytes) | Minimum Value Signed | Minimum Value Unsigned | Maximum Value Signed | Maximum Value Unsigned |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
TINYINT | 1 | -128 | 0 | 127 | 255 |
SMALLINT | 2 | -32768 | 0 | 32767 | 65535 |
MEDIUMINT | 3 | -8388608 | 0 | 8388607 | 16777215 |
INT | 4 | -2147483648 | 0 | 2147483647 | 4294967295 |
BIGINT | 8 | -263 | 0 | 263-1 | 264-1 |
DECIMAL
The DECIMAL (also implemented as NUMERIC) data type in MySQL stores exact numeric data values. It is used when it is important to preserve exact precision, for example with monetary data.
Consider the following example
salary DECIMAL(5,2)In this example, 5 is the precision and 2 is the scale. The precision represents the number of significant digits that are stored for values, and the scale represents the number of digits that can be stored following the decimal point.
So values that can be stored in the salary column range from -999.99 to 999.99.
The syntax DECIMAL(M) is equivalent to DECIMAL(M,0). Similarly, the syntax DECIMAL is equivalent to DECIMAL(10,0) i.e the default value of M is 10.
Note: If the scale is 0, DECIMAL values contain no decimal point or fractional part.
The maximum number of digits for DECIMAL is 65.
If a column is assigned a value with more digits following the decimal point than are permitted by the specified scale, the value is converted to that scale.
FLOAT, DOUBLE and REAL
For floating-point types MySQL permits a nonstandard syntax: FLOAT(M,D) or REAL(M,D) or DOUBLE(M,D).
Here, (M, D) means that values can be stored with up to M digits in total, of which D digits may be after the decimal point.
For example:
salary FLOAT(6,2)Here the value of salary can range from -9999.99 to 9999.99.
It is important to note that if you insert 9999.009 into a FLOAT(6,2) column, MySQL rounds it off to 9999.01 because floating-point values are approximate and not stored as exact values.
Note: As of MySQL 8.0.17, the nonstandard FLOAT(M, D) and DOUBLE(M, D) syntax is deprecated and support for it will be removed in a future MySQL version.
Before we wrap up Numeric data types, let us see some synonyms of certain MySQL data types that are frequently used
INTis synonym ofINTEGERDECandFIXEDare synonyms forDECIMALREALandDOUBLEare synonyms forDOUBLE PRECISION.
String Data Types in MySQL
MySQL supports the following string data types: CHAR, VARCHAR, BINARY, VARBINARY, BLOB, TEXT, ENUM, and SET.
Let’s see in detail each string data type of MySQL.
CHAR and VARCHAR
The CHAR and VARCHAR types are similar but differ in the way they are stored and retrieved.
They also differ in maximum length and in whether trailing spaces are retained.
The CHAR and VARCHAR types are declared with a length that indicates the maximum number of characters you want to store. For example, CHAR(30) can hold up to 30 characters.
The length of a CHAR column is fixed to the length that you declare when you create the table. The length can be any value from 0 to 255. When CHAR values are stored, they are right-padded with spaces to the specified length. When CHAR values are retrieved, trailing spaces are removed unless the PAD_CHAR_TO_FULL_LENGTH SQL mode is enabled.
Values in VARCHAR columns are variable-length strings. The length can be specified as a value from 0 to 65,535. The effective maximum length of a VARCHAR is subject to the maximum row size.
If strict SQL mode is not enabled and you assign a value to a CHAR or VARCHAR column that exceeds the column’s maximum length, the value is truncated to fit and a warning is generated.
Consider the following table, whatever be the length of the value for CHAR(4) type the storage required is always 4 bytes whereas for VARCHAR(4) the storage required depends on the value’s length.
| Value | CHAR(4) | Storage Required | VARCHAR(4) | Storage Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|
'' | ' ' | 4 bytes | '' | 1 byte |
'ab' | 'ab ' | 4 bytes | 'ab' | 3 bytes |
'abcd' | 'abcd' | 4 bytes | 'abcd' | 5 bytes |
'abcdefgh' | 'abcd' | 4 bytes | 'abcd' | 5 bytes |
That’s why VARCHAR should be preferred when the size of the string column is not fixed. It could save a lot of storage space.
It is important to note in the above table that MySQL was not working in strict mode otherwise the last row value which exceeds column length should not have been stored in the table.
BINARY and VARBINARY
The BINARY and VARBINARY types are similar to CHAR and VARCHAR, except that they store binary strings rather than nonbinary strings. That is, they store byte strings rather than character strings.
BLOB and TEXT
A BLOB (Binary Large Object) is a MySQL data type that can store binary data such as images, multimedia, and PDF files.
The four BLOB types are TINYBLOB, BLOB, MEDIUMBLOB, and LONGBLOB. These differ only in the maximum length of the values they can hold.
| Data Type | Max Storage Space |
|---|---|
TINYBLOB | 255 bytes |
BLOB | 65,535 bytes |
MEDIUMBLOB | 16,777,215 bytes |
LONGBLOB | 4,294,967,295 bytes |
Depending on the max possible size for a particular column the appropriate BLOB should be chosen.
For example, if you know that no image could exceed 65,533 bytes of space then you should use BLOB type
CREATE TABLE my_photo (id int PRIMARY KEY, PHOTO blob);BLOB values are treated as byte strings (binary strings) that’s why it is considered as MySQL String Data Types.
TEXT type in MySQL is used to store long-form text strings because it is treated as character strings.
The four TEXT types are TINYTEXT, TEXT, MEDIUMTEXT, and LONGTEXT. Again these differ only in the maximum length of the values they can hold.
| Data Type | Max Storage Space |
|---|---|
TINYTEXT | 255 characters |
TEXT | 65,535 characters |
MEDIUMTEXT | 16,777,215 characters |
LONGTEXT | 4,294,967,295 characters |
It may seem to you that TEXT is similar to VARCHAR and BLOB is similar to VARBINARY type in MySQL, but they differ from them in the following ways
- For indexes on
BLOBandTEXTcolumns, you must specify an index prefix length. ForCHARandVARCHAR, a prefix length is optional. BLOBandTEXTcolumns cannot haveDEFAULTvalues.
ENUM and SET
ENUM in MYSQL is a string type that allows values to be chosen only from the permitted list.
Consider the following example
CREATE TABLE shirts (
name VARCHAR(40),
size ENUM('x-small', 'small', 'medium', 'large', 'x-large')
);
INSERT INTO shirts (name, size) VALUES ('dress shirt','large');As you can see, the column ‘size’ cannot have values other than what has been specified inside ENUM.
So by using ENUM we can restrict a particular column to have a limited set of possible values.
whereas, SET in MySQL can have zero or more values, each of which must be chosen from a list of permitted values specified when the table is created.
Consider the following examples
CREATE TABLE shirts (
name VARCHAR(40),
size SET('x-small', 'small', 'medium', 'large', 'x-large')
);Query OK, 0 rows affected (1.39 sec)
INSERT INTO shirts (name, size) VALUES ('dress shirt','large, x-small, fit');ERROR 1265 (01000): Data truncated for column ‘size’ at row 1
We got an error because MySQL is running in strict mode and we tried to insert ‘fit’ into the size column which was initially not defined when creating a table.
If we again try by removing the ‘fit’ from the INSERT statement then we observe that the query is successful.
INSERT INTO shirts (name, size) VALUES ('dress shirt','large,x-small');Query OK, 1 row affected (0.11 sec)
SELECT * FROM shirts;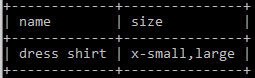
In non-strict mode, MySQL automatically truncates the items which are not defined in the set and inserts the rest with a warning.
Date and Time Data Types in MySQL
MySQL has the following date and time data types for representing temporal values: DATE, TIME, DATETIME, TIMESTAMP, and YEAR.
Let’s see each of them in detail.
DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP
The DATE, DATETIME, and TIMESTAMP types in MySQL are very much similar to each other.
The DATE type is used for values with a date part but no time part.
The format for DATE type is ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ and the supported range is ‘1000-01-01’ to ‘9999-12-31’.
The DATETIME and TIMESTAMP type is used for values that contain both date and time parts.
The format for DATETIME and TIMESTAMP is ‘YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss’.
The supported range for DATETIME is ‘1000-01-01 00:00:00’ to ‘9999-12-31 23:59:59’ and for TIMESTAMP is ‘1970-01-01 00:00:01’ UTC to ‘2038-01-19 03:14:07’ UTC.
The following example illustrates the use of TIMESTAMP data type.
CREATE TABLE posts (id int PRIMARY KEY, content TEXT, timestamp TIMESTAMP);
INSERT INTO posts (1, 'This is my first post', '2020-08-30 05:10:07');TIME
TIME type in MYSQL is used to store and retrieve data in the form of ‘hh:mm:ss’.
TIME values may range from ‘-838:59:59’ to ‘838:59:59’.
The hours part may be so large because the TIME type can be used not only to represent a time of day (which must be less than 24 hours), but also elapsed time or a time interval between two events (which may be much greater than 24 hours, or even negative).
YEAR
YEAR type in MySQL is used to store and retrieve year value.
MySQL display YEAR in form of ‘YYYY' and it ranges from 1901 to 2155.
YEAR accepts input values in a variety of formats:
- As 4-digit strings in the range ‘1901’ to ‘2155’.
- As 4-digit numbers in the range 1901 to 2155.
- As 1- or 2-digit strings in the range ‘0’ to ’99’. MySQL converts values in the ranges ‘0’ to ’69’ and ’70’ to ’99’ to
YEARvalues in the ranges 2000 to 2069 and 1970 to 1999. - As 1- or 2-digit numbers in the range 0 to 99. MySQL converts values in the ranges 1 to 69 and 70 to 99 to YEAR values in the ranges from 2001 to 2069 and 1970 to 1999.
- The result of inserting a numeric 0 has a display value of 0000 and an internal value of 0000. To insert zero and have it be interpreted as 2000, specify it as a string ‘0’ or ’00’.
- As the result of functions that return a value that is acceptable in
YEARcontext, such asNOW().
If strict SQL mode is not enabled, MySQL converts invalid YEAR values to 0000. In strict SQL mode, attempting to insert an invalid YEAR value produces an error.
The other MYSQL data types such as spatial and JSON are out of scope of this post. If you are interested to know about them then I recommend you to refer to the official documentation.
In this post, we have discussed several MySQL data types in detail. These data types help us in determining what type to use for efficient storage and retrieval of data in MySQL.
