IPV6 Protocol Header

Version: (4bits)Always set to 6.
Traffic Class: (8bits).A dscp value for qos(quality of service).
Flow Label: (20bits)Identifies unique flows.
Payload Length: (16bits)length of the payload in bytes.
Next Header: (8bits)header or protocol which flows.
Hop Limit: (8bits)similar to ipv4 time to live field.
source Address: (128bits)source ip address.
Destination Address: (128bits)destination ip address.
Comparison Between IPv6 VS IPv4 Packet Headers
- The header length field is eliminated in ipv6 because the length of the header is fixed in this version.
- The service kind field is eliminated in ipv6. The priority and flow label fields along take over the operation of the service kind field the function of the service type field.
- The total length is eliminated in ipv6 and replaced by the payload length field.
- The identification, flag, and offset fields eliminated from the bottom header in ipv6. They are enclosed within the fragmentation extension header.
- The TTL field is termed hop limit in ipv6.
- The protocol field is replaced by the future(next) header field.
- The header checksum is eliminated because the checksum is provided by the upper-layer protocols, it is therefore not needed at this level.
- The option fields in ipv4 are enforced as extension headers in ipv6.
Comparison Between IPv6 VS IPv4 Extension Headers
- The no operation and end of option in ipv4 is replaced by pad1 and padN options in ipv6.
- The record route possibility isn’t enforced in ipv6 as a result of it had been not used.
- The timestamp possibility isn’t enforced as a result of it had been not used.
- The source route option is called the source route extension header in ipv4.
- The fragmentation fields within the base header section of ipv4 have touched to the fragmentation extension header in ipv6.
- The authentication extension header is new in ipv6.
- The encrypted security payload extension header is new in ipv6.
Advantage of IPv6 over IPv4
- Larger Address Space: An IPv6 address is 128 bits, as we discussed before. Compared with a 32-bit address of IPv4, this is a huge (296) increase in the address space.
- higher Header Format: IPv6 uses a replacement header format within which options square measure separated from the bottom header and inserted, when needed, between the bottom header and upper-layer knowledge. This simplifies and hastens the routing method as a result of most of the options that oughtn’t to be checked by routers.
- Allowance of extension: IPv6 is intended to permit the extension of the protocol if needed by new technologies or applications.
- Support for Resource Allocation: In IPv6, the type-of-service field has been removed, however, a mechanism (called flow label) has been added to modify the supply to request special handling of the packet. This mechanism is wont to support traffic like period audio and video.
- Support for additional Security: The coding and authentication options in IPv6 offer confidentiality and integrity of the packet.
IPv4 To IPv6 Transition
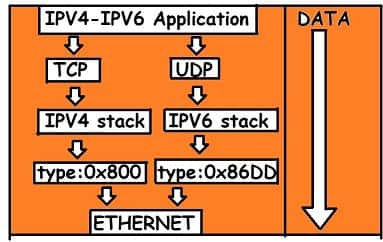
Because of the large range of systems on the net, the transition from IPv4 to IPv6 cannot happen suddenly. It takes a substantial quantity of your time before every system within the web will move from IPv4 to IPv6.
The transition should be swish to forestall any 20.56 IPv6. The transition should be swish to forestall any problems between IPv4 and IPv6 systems.
