Problem: Write a Java program to convert a decimal number into its corresponding octal representation.
Example:
Input: 7 Output: 7 Input: 8 Output: 10
Method 1: Using While Loop
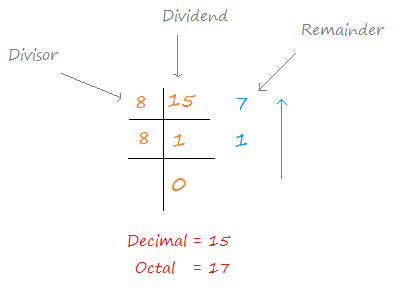
To convert a decimal into octal we divide the decimal number by 8 until it reduces to 0 and stacks the sequence of remainders in a bottom-up manner.
In the Java program, we divide and concatenate remainders inside a while loop as follows:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int octal=0, i=1, remainder;
//Input the decimal number
System.out.println("Enter a Decimal Number");
int decimal = in.nextInt();
//loop until the decimal is not 0
while(decimal>0){
remainder = decimal%8; //compute remainder
octal += i*remainder; //concatenate remainders to the octal
decimal = decimal/8; //update decimal with quotient
i=i*10; //multiply 10 to i
}
//output the octal number
System.out.println("Octal: "+octal);
}
}Output:
Enter a Decimal Number
15
Octal: 17
To concatenate remainders in a bottom-up manner, we first multiply the remainder with 10number_of_digits_in_octal (i*10) then add it to the octal number.
Method 2: Using Recursion
We can also convert a decimal number into an octal number using the recursive approach.
To do so, we recursively call the function with the quotient value (decimal/8) and print the remainder after the recursive call.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
//Input the decimal number
System.out.println("Enter a Decimal Number");
int decimal = in.nextInt();
System.out.print("Octal: ");
decToOctal(decimal); //call the recursive function
}
private static void decToOctal(int n){
if(n>0){
//recall by passing quotient
decToOctal(n/8);
//output the remainder
System.out.print(n%8);
}
}
}Output:
Enter a Decimal Number
8
Octal: 10
By writing the print statement after the recursive call statement, the remainders gets printed in the bottom-up sequence.
It is so because the print action starts when the recursive function starts tracing back to its first recursive call.
